Advertisement
On Wednesday, the Federal Reserve made an announcement to fight Inflation that would raise its benchmark interest rate by 0.75 percent. This was like a sharp rise after a similar move in 1994.
At the end of the first weeks, the Federal Open Market Committee set the exchange rate and put its fund rate at 1.5% – 1.75%. The benchmark interest rate hit its highest level since before the Covid pandemic broke out in March 2020.
The stock codes have had certain fluctuations since that decision was made. Stocks edged higher when Fed Chairman Jerome Powell spoke at a news conference after concluding his meeting.
Powell argues that today's 75 basis point level is a fairly unusual increase and he does not expect the move at this scale to continue and be popular. He added that he still expects that at the upcoming July meeting there will be a 50 or 75 basis point increase. Decisions will be made during the meetings and the Fed will announce the upcoming moves in the clearest and most specific way.
Since 1991 the federal funding rate has been in effect.
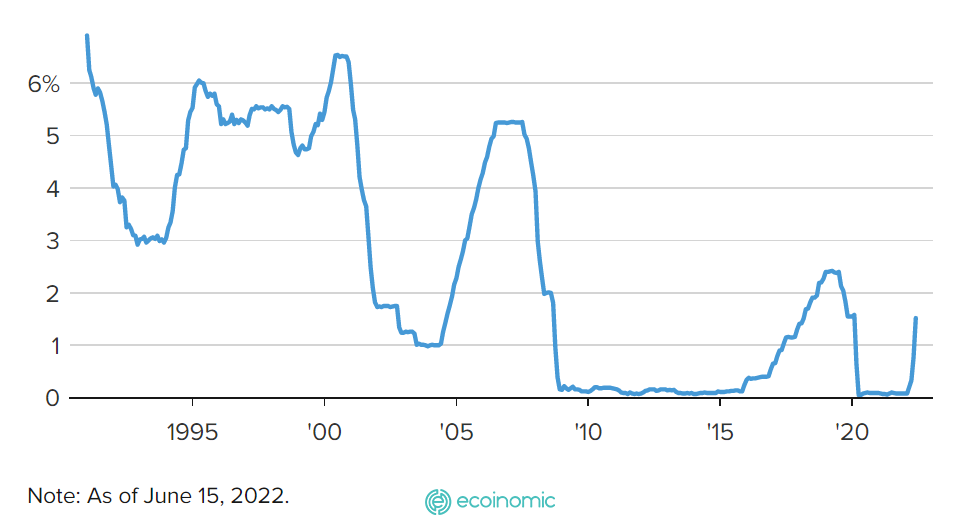
FOMC members point to a stronger path of rate hikes than before aimed at preventing stronger and faster inflation since December 1981.
The Fed is expected to stop its annual benchmark interest rate at 3.4 percent at the midpoint of its target range on expectations. Compared to the March estimate, the correction was up 1.5 percentage points. The commission said the rate could rise to 3.8 percent by 2023.
Reduce expected growth in 2022
The authorities have minimized the expected growth of the economy in 2022, predicting GDP to grow only 1.7% and will decrease by 2.8% compared to March.
How experts forecast inflation to rise from 4.3% to 5.2% this year. This is the level of inflation calculated according to personal consumption. However, this is core inflation that does not include the cost of food and energy. Core PCE inflation hit 4.9% in April which will lead to forecasts of a reduction in price pressures over the next month.
The commission's statement has made the overall picture of the economy more optimistic in the context of rising inflation.
The estimates adopted a summary of the committee's economic forecasts have shown inflation to fall sharply in 2023. The forecast will drop to 2.6% – 2.7%, the expectation is less changed than in March.
Almost all FOMC members approved with the statement with the exception of Fed President Esther George, who only wanted a smaller gain.
Fund ratios can also drive higher rates on savings accounts and CDs, although the process of depositing money into it often takes longer.
Commit to the 2% inflation target
Central banks have moved to use the fund exchange rate to try to slow the economy with the aim of adjusting demand levels so that supply can catch up.
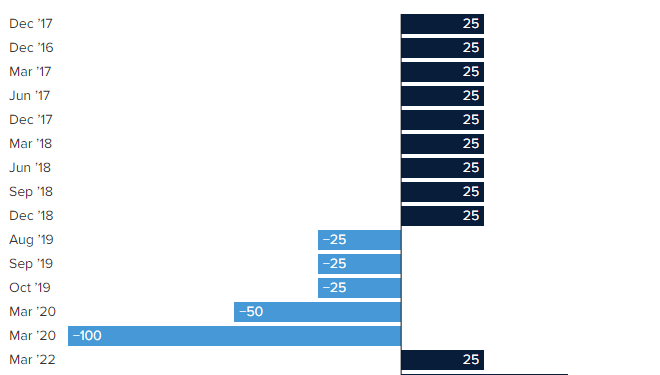
The ongoing policy tightening with economic growth has slowed while prices have still risen this has caused so-called stagnant inflation.
First-quarter growth declined continuously at a rate of 1.5%. Two consecutive quarters of negative growth, the thumb rule has been widely used to determine recessions. Policymakers have stressed that it will be possible to raise by half a point or 50 basis points to help curb inflation.
In May, inflation as measured by the consumer price index rose 8.6 percent annually. In addition, retail sales were announced on Wednesday with sales down 0.3 percent in a month and inflation rising another 1 percent.
The strength of the economy is the job market, although May's increase was the lowest since April 2021. Average hourly earnings have increased as inflation-adjusted declines by 3% compared to the previous one. —
Telegram: https://t.me/+XqnDmxy-bz0wMTE1
Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/655607162536305
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/WikiBinancecom
Twitter: https://twitter.com/wikibinancevn
















