Advertisement
The origin of the P2P network?
P2P stands for Peer-to-Peer, a type of distributed network application that dates back to the 1980s when they were first deployed for business purposes. However, the concept was introduced to the public in 1999 when college student Shawn Fanning created a Napster music-sharing service.
The service quickly became an unauthorized sharing platform for copyrighted songs. But two years later, Napster was shut down by lawmakers due to a lawsuit from the U.S. music industry. This has given rise to a new concept of P2P service that wants to fill the gap and continue to develop decentralized networks.
Today, the model is leveraged in web search engines, online marketplaces, streaming platforms, P2P Blockchain, and IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) web protocols. P2P is at the core of blockchain technology, with the introduction of cryptocurrencies has added many new uses.
What is P2P (Peer-to-Peer)?

Peer-to-peer is a decentralized communication model between two Peer-to-Peer networks also known as nodes, which can communicate with each other without a central server. Unlike the seeder/leecher (or client/server) model in which the seeder makes requests and the leecher meets requirements, the network model allows each party to act as a seeder and leecher. This means that after the network is formed, participants can use it to share and store files without the help of an intermediary.
How does it work?
In essence, the Peer-to-Peer network is maintained by a distributed user network, independent of the central administrator or server. Each node stores a copy of the files and acts as a client server for other nodes.
Therefore, each node can download files from other nodes or upload files to other nodes. This is the difference between peer-to-peer networks and traditional server-client systems.
On the P2P network, connected devices share files stored on their hard drives. Using software applications designed to mediate data sharing, users can query other devices on the network to find and download files. Once a user has downloaded a file, they can act as the source of that file.
In other words, when a node acts like another machine, they download files from other nodes on the network. But when they act as a server, they are the source from which other nodes can download files. However, in practice, nodes can perform two functions at the same time (e.g., downloading file A and uploading file B).
Peer-to-peer network models
The P2P network is unstructured.
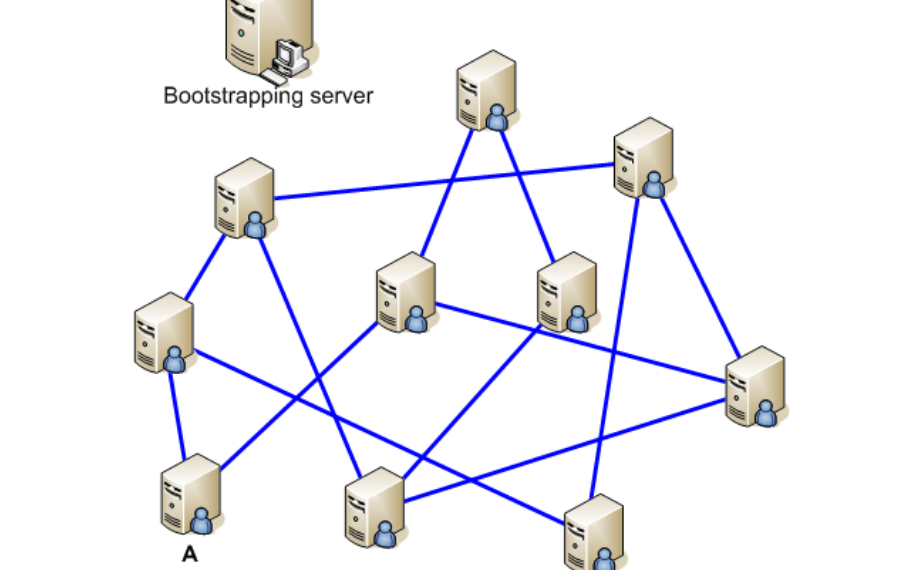
network, the nodes connect and communicate randomly.
Since nodes frequently join and leave the network, these systems are best suited for high-churn operations. For example, a social platform deployed on an unstructured P2P network can use it effectively, as users can choose to join or leave the network regularly.
Such networks are easy to build. However, they require high CPU and memory usage because search queries are sent to the entire network. Therefore, if only 5% of computers have what you are looking for, then it may take a while.
Structured P2P network
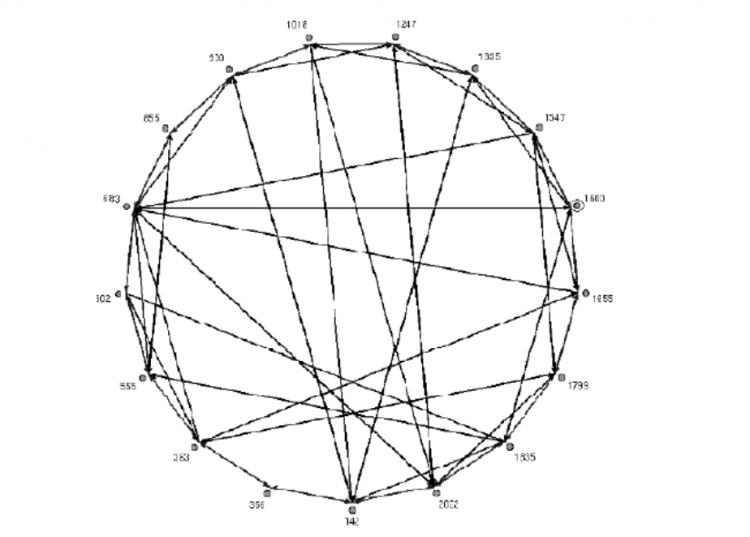
On the other hand, structured networks are organized in a way that allows nodes to search for files efficiently, even if the data is not widely stored.
In most cases, these networks deploy a distributed hash table (DHT), which allows nodes to search for data using hashes. Although structured networks can route traffic efficiently, they require higher setup and maintenance costs and tend to be more focused.
Combined P2P network
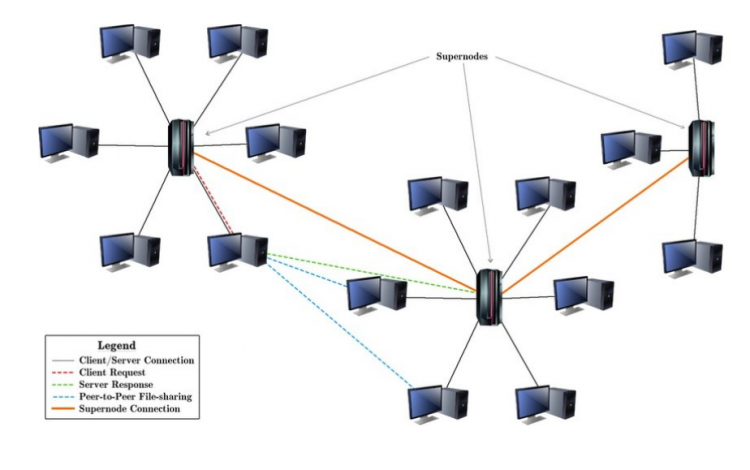
A combined network combines a peer-to-peer model and a client/server on a single platform.
The network uses an index server that contains data about the location of the resources at the center and uses this server to search. The centralized functionality provided by the structured network and the equality of the node is provided by the unstructured network responsible for creating the balance on the combined network. This type of network works better than its rivals because certain search queries require a centralized functionality but can at the same time benefit from decentralized networks.
P2P Network Application in Blockchain
The concept of blockchain was popularized in 2008, as part of a proposal for Bitcoin. Bitcoin’s creator Satoshi Nakamoto has defined it as a “peer-to-peer cryptocurrency system” built with the aim of creating a form of P2P digital currency without the need for a bank.

Blockchain technology basically leverages the power of the P2P network and provides a shared and reliable transaction ledger. As a distributed ledger technology, blockchain records transactions as a digital block with an immutable time stamp indicating the sender and recipient. There is no Supervisory Authority that manages blockchain networks, and only participants can authenticate transactions between each other. This new form of distributed data storage and management acts as a digital ledger that publicly records all transactions and activities.
What is the P2P cryptocurrency exchange?
P2P cryptocurrency exchanges allow users to buy or sell directly with another user. Unlike centralized exchanges, where you have to complete KYC to process orders, most P2P exchanges allow you to send/receive cryptocurrencies without requiring you to verify your identity. In addition, P2P-based exchanges have no disadvantages like centralized exchanges.
How does the P2P cryptocurrency exchange work?
Users can usually register with the exchange without having to verify their identity. Registration only requires one email address and one password. After registration, users can make various buy and sell offers posted by individuals on the platform. Each offer has different payment options, different rates, and usually the minimum or maximum purchase amount. The buyer can choose an offer and contact the seller to set up the transaction. If you are a seller, you can post the accepted payment method as well as any related fees. In general, P2P cryptocurrency exchanges use margin accounts to send cryptocurrencies or other collateral from users to ensure the safety of the platform.
See also: How To Identify And Avoid Scams On Binance P2P
Advantages of the network
The structure of the P2P network is maintained by its users, whose cps can both provide and use resources. There is no such thing as a central server or host server, which makes P2P systems very different from traditional client-server models, where data is distributed one way (from the centralized server to its clients), since this structure the P2P network offers some of the following advantages to the user:
- The P2P network does not need a network operating system.
- There is no need for an expensive server as individual workstations are used to access data files.
- There is no need for professional staff like network technicians.
- Much easier to set up than the client-server network, which does not require much professional knowledge.
- If a computer fails, it will not interrupt any other part of the network.
Disadvantages of the network
- Since the computer can be accessed by others, it can slow down the user’s performance.
- Files and folders cannot be centrally backed up.
- Unorganized files and resources focus on a specific “shared area.” They are stored on individual computers and can be difficult to determine if the computer owner does not have a reasonable storage system.
- If the virus enters the network, there will be a lot of users affected.
- The resources will disappear because the resource supply node is disconnected at any time.