Advertisement
Along with the expansion of blockchain, lending and borrowing platforms are considered as decentralized banks in the DeFi ecosystem that promote the flow of money and the development of the entire market.
Let’s find out the mechanism of lending – borrowing in DeFi through the article below!
What is lending?
Lending is a form of lending cryptocurrency to receive an annual percentage yield (APY).
Unlike traditional lending, lending is not regulated by any intermediary or government. Instead, smart contract automates the entire process, allowing users to lend any crypto asset by depositing the assets into the smart contract via the DeFi protocol and earning passive profits.
What is borrowing?
Borrowing is a form of borrowing cryptocurrency for a certain period of time.
To meet basic requirement for DeFi borrowing, have to deposit tokens into the protocol as collateral to provide liquidity. After the expiration of the term, the user will have to pay the principal asset and interest as originally committed.

Types of loans
Mortgage
Typically, users will have to provide tokens in the protocol as collateral to ensure repayment capacity.
If there is a change in price, the user must add collateral to ensure the asset is not liquidated.
Flash loan
Flash loan is a form of loan that does not require collateral but the loan must be repaid in the same transaction. The transaction will be canceled before being validated in a block if the loan and interest are not repaid on time.
Flash loan is often used for collateral swap and Arbitrage trading.
>>> Related: What is Flash loan?
The mechanism of lending – borrowing
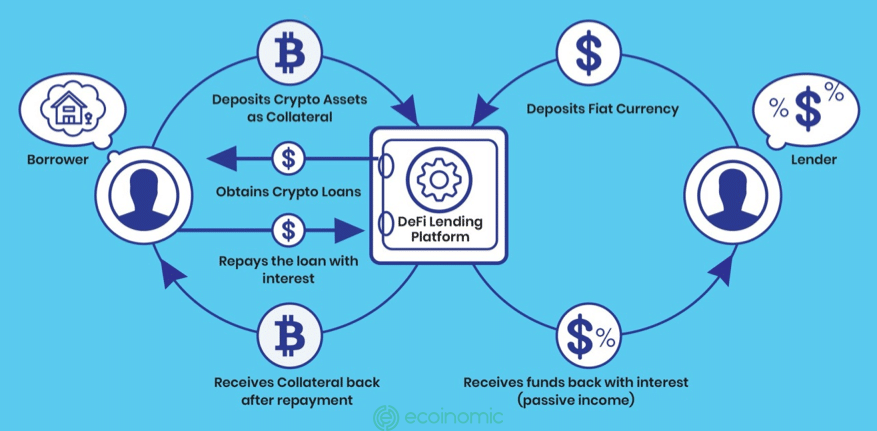
There are 3 entities participating in the DeFi lending – borrowing ecosystem:
- DeFi Lending Protocol
- Borrower
- Lender
Decentralized cryptocurrency lending protocols serves as intermediaries connecting lenders with borrowers through smart contract to automate payments and loan yields.
The borrower will use the crypto asset as collateral to receive the loan and repay it with interest in a certain period of time. Although the borrower still has ownership of collateral, it is not possible to make transactions.
The borrower will receive a loan immediately, while the lender will earn a passive income from the interest of the loan. If the borrower fails to repay the debt, the collateral will be liquidated to pay off the loan.
Related: Margin And Futures On Binance – What Are The Differences?
Indicators to pay attention to when participating in lending – borrowing
- APY: Annual percentage yield includes compound interest. The interest rate of stable coins such as ETH, BTC is usually lower than new coins.
- APR: Annual percentage rate does not include compound interest.
- Loan duration: Loan terms vary depending on each platform such as 7 days, 14 days or 90 days.
- Total value locked (TVL): The total value of assets sent to the protocol.
- Loan to value (LTV): The ratio between the loan value and the collateral value. Risk is assessed based on repayment liquidity, so the higher the LTV, the greater the lender’s risk.
- Minimum collateralization ratio: MakerDAO has a minimum collateralization ratio of 150%, when users stakes assets worth $150, they will be able to Borrow $100. Meanwhile, Compound’s minimum mortgage ratio is 133%.
- Liquidation point: When the collateralization ratio is too low and reaches the liquidation mark, the protocols enable the asset liquidation mechanism to ensure the safety of the protocol.
- Liquidation bonus: With the aim of incentivizing participation, liquidators will receive liquidation bonus when assets are liquidated due to borrowers’ inability to repay debts.
- Liquidation penalty: The borrower’s penalty when the property is liquidated.
- Capital utilization: It indicates which protocol can lend more based on the same amount of capital.
Opportunities and risks of lending – borrowing
Opportunities
- Low interest rate: Cryptocurrency loans have lower interest rates than bank loans.
- No credit check: Cryptocurrency lending platforms usually do not require a credit check, those who have bad credit history or are ineligible for a bank loan can still secure a loan.
- Fast processing speed: Smart contracts will automate and manage loans, speeding up the lending and borrowing process. Once approved, you can receive your loan in just a few hours.
- Passive income: Users will generate passive income from a loan at an interest rate that is usually much higher than traditional savings.
- Optimizing capital efficiency: Users can stake long-term holdings to borrow other tokens for their own use.
Risk
- Devaluation risk: The price of the coin falls during the lending process, causing the interest rate the lender receives not to make up for the deficit. Besides, borrowers will face the risk of liquidating assets when the price of collateralized coins/tokens drops suddenly.
- Flash loan attack: Hackers take advantage of protocol vulnerabilities, borrow huge amount of cryptocurrencies for the purpose of manipulating the market. For example: the attack on the PancakeBunny protocol, hackers borrowed a large amount of BNB to manipulate the price of BUNNY then dumped it, causing the token to drop by 96%.
- Rug pull: Developers withdraw all liquidity in the liquidity pool or discharge all tokens and abandon the project after raising capital from investors. For example, in 2021, DeFi Compounder Finance had a rug pull worth more than $10.8 million, $4.8 million in Ether, $5 million in Dai, and $750,000 in Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) were withdrawn from the platform.
Outstanding lending and borrowing protocols
Aave
Aave is an DeFi protocol on Ethereum that allows users to borrow up to 67% of the value of collateral with more than 15 cryptocurrencies. Users will deposit cryptocurrencies into the platform through a Web3 wallet, then they will receive an equivalent number of aTokens.
aToken can be stored, swapped, and traded freely, allowing users to access to a variety of cryptocurrencies. Aave offers both stable and variable interest rates with exchange rate conversion services.
Aave’s special mechanism is flash loan that allows users to borrow cryptocurrencies immediately without any collateral. Flash loan requires a fee of 0.09%,. The time to complete the transaction is only 13 seconds and the original loan must be repaid in just one Ethereum transaction.

MakerDAO
MakerDAO serves as a loan credit facility with a predetermined interest rate. MarketDAO uses the DAI stablecoin to determine the loan interest rate, repayment amount, and MKR tokens to control the MakerDAO.
DAI is created whenever users deposit cryptocurrency into the Maker Vault. Users can also accumulate interest by Staking borrowed DAI in the platform. The better the cryptocurrency collateral is established, the greater the amount of Dai users can borrow with a lower interest payment.
Besides, users can use DAI to buy more collateral and increase positions up to 100%.

Compound
Compound is a DeFi protocol that allows users to borrow up to 75% of collateral with a variety of cryptocurrencies and stablecoins, including ETH, DAI, USDC, USDT, and BAT. Deposits in the protocol will be transferred to the liquidity pool so users can make collateral to borrow tokens.
The lender will receive CTokens representing the deposit or the underlying asset value. Interest rates will vary depending on the cryptocurrency, the stability of the collateral and any fluctuations in the global cryptocurrency market.

Conclusion
Hopefully, through the above article, Ecoinomic has helped you understand the mechanism of prominent lending – borrowing protocols in the DeFi ecosystem.
Lending – Borrowing offers opportunities to take advantage of cash flow and generate passive income or arbitrage trading. However, investors need to thoroughly assess the potential risks in order to implement the right investment strategy and optimize their portfolio.