Advertisement
Gas fee – A factor that gives many users a headache when trading. The cost of gas fees is too high or unreasonable will greatly affect the profitability of the transaction. High fees also make many people hesitate whenever they want to do retroactive or interact with smart contracts. Especially on the Ethereum exchange, which has towering fees. The article below will help you better understand Gas Limit, Gas Price as well as how to optimize the costs when trading.
How to recognize Gas Limit, Gas Price
Gas Limit
Gas Limit is the maximum amount of gas that a user is prepared to pay for an entertainment activity or confirm a transaction payment. Gas Limit’s default value depends on the term and type of transaction payment. Users are entitled to set up Gas Limit.
The necessity of Gas Limit to complete a transaction payment thanks to the complexity of that transaction payment. The more complex the transaction, the more measurement and statistical resources it consumes, and therefore the more gas consumed.
Gas Price
Gas Price is the amount of money in the original coin of that blockchain that the user is willing to spend per unit of Gas. Gas prices will affect the speed of miner/validator transaction confirmations in the network and put them into the new block.
- The higher the gas price ⇒ the higher the miner/validator reward ⇒ your transaction will be confirmed by miner/validator.
- The lower the gas price ⇒ users will have to wait longer. In case you’re not in a hurry, you can also save by paying a lower gas price.
Particularly for the Ethereum blockchain, gas prices will be calculated in Gwei units. Gwei is a face value of ETH. Accordingly, each Gwei equals 0.0000000001 ETH (10-9 ETH). So instead of saying Gas Free is 0.0000000001 ETH 1 in a long and easy way to mistake. We can replace it with Gas Fee = 1 Gwei for quick.
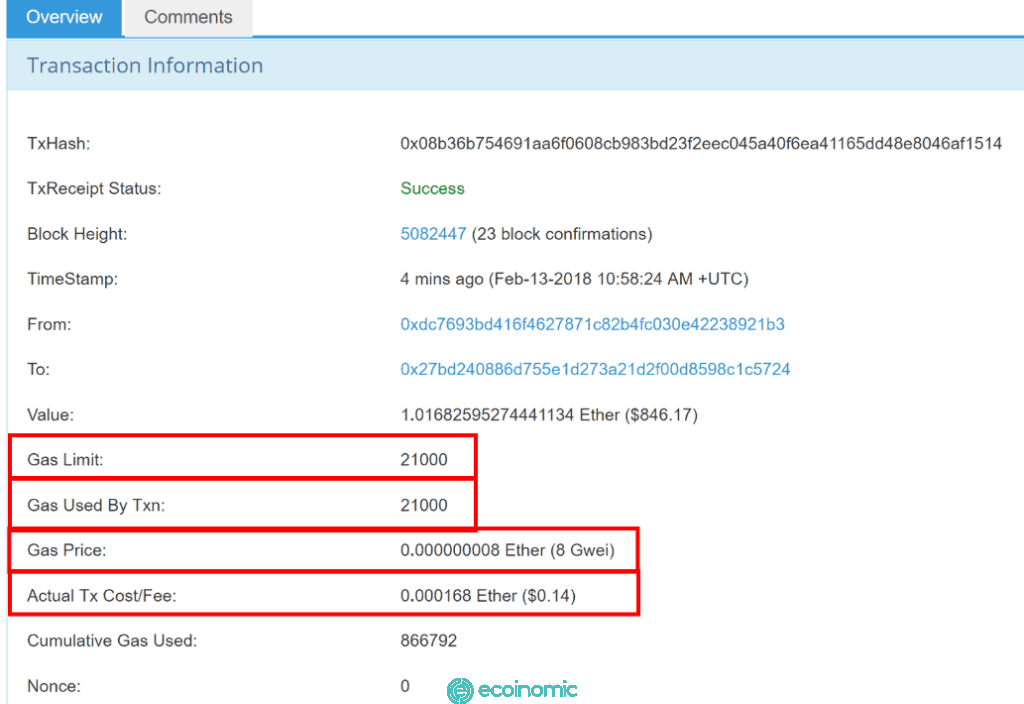
For example, Gas Limit Ethereum is 21,000 and Gas Price is 106 Gwei.
Thus: Gas Fee = 21,000 x 106 Gwei = 2,226,000 Gwei ~ 0.002226 ETH. That is, you need to pay 0.002226 ETH to make the transaction.
What is gas fee?
Gas fee or gas fee is the term for a type of transaction fee that we need to pay when trading. In particular, gas is the unit that measures the energy needed to make a transaction on the network.
Just like riding a gasoline-filled motorcycle, when trading blockchain, you also need gas to be able to make transactions.
As such, gas will be used to:
- Make smart contracts.
- Run decentralized apps
- Pay for data storage.
- Complete the transaction
For example, to run 10km, you need to use 0.5 liters of gasoline equivalent to 15,000 VND. In Blockchain and Crypto, if you want to trade 100 ETH via the Ethereum network wallet. You will need to pay a certain amount of gas. And this gas will be converted to ETH.
Gas Charges on Blockchains
When trading on any blockchain, we have to pay gas fees in the equivalent coin on it. In other words, when making transaction payments or wanting to transfer tokens in any blockchain, teammates will use the original coin of that Blockchain to pay the transaction payment fee.
This means that depending on the different blockchain platform, gas fees are also charged in different units. Users who want to pay transactions on any blockchain must protect their friends who have the original coin of that Blockchain as Gas. Specifically:
- Want to trade on Ethereum: Buy, sell, store ERC20 tokens such as ETH, USDT ERC20,…. ⇒ Pay Gas Fee in Ethereum (ETH).
- Want to trade on Solana: Buy, sell, store SPL tokens such as SRM, RAY,… ⇒ Pay Gas Fee in Solana Bronze (SOL).
- Want to trade on Binance Smart Chain: Buy, sell, store BEP20 tokens,… ⇒ Pay Gas Fee in Binance Coin (BNB).
Tips for optimizing gas costs when trading

When trading on any blockchain, I have to pay gas fees in equivalent coins on which you can completely save gas costs from the tips below:
- Optimize the trading steps: Use the necessary operations, as little as possible. Because one more step at a time, you’re going to spend gas to do it.
- In advance, to avoid transaction failures and additional costs, you should use scan websites to refer to transaction fees and choose a cheap gas time to conduct transactions. Typical: BSCscan for Binance Smart Chain, EtherScan for Ethereum,…
- Network density monitoring: To avoid network congestion, high gas fees and the risk of making failed transactions, monitor the transaction density before proceeding. For example, before trading on Ethereum, you can check transaction density information on https://ethereumprice.org/gas/.
- Change the blockchain network to transact: If that coin or token is supported on many different chains, choose the chain with transaction optimization and low fees. . For example, if you transfer USDT, the advice is that you should use a TRC20 network that will incur a much lower fee than using the ERC20 network.
- Use the upgrade of the Blockchain: for example ETH 2.0 will launch and ensure transaction fees will decrease.
Conclusion
Gas Free is a concern for users when entering the crypto market. The founders of the Blockchain system network did not expect the cost to be too high, which we all see clearly on Ethereum’s Blockchain network at the time of the explosion of the DeFi market. Currently, Ethereum is holding investors and real estate projects through a promotion to ETH 2.0, but whether gas fees will be fully processed remains an unanswered question.
Let’s look forward to eth’s most important update, and within that time we can all use another repair replacement network with cheaper fees, binance smart chain grown by the world’s largest exchange payments exchange Binance.