Advertisement
Coin mining is one of the popular forms of profit in the cryptocurrency market. Not only operating alone, but miners also gather together called Mining Pool. The following article, ecoinomic.io will explain this term.
Why is Mining Solo a less profitable activity?
Like actual mining, cryptocurrency mining is a risky activity that consumes a lot of energy. The difference is that cryptocurrency miners do their operations on a digital platform using computational resources to solve complex mathematical puzzles.
The first miner to solve the puzzle will verify the latest transactions and add a new Block to the Blockchain. In return, miners receive rewards in the form of newly mined coins and fees are charged on each verified transaction. Therefore, the success of a miner depends on their ability to solve these puzzles before other miners do.
However, as mentioned earlier, this process takes place that will consume a lot of capital and energy. Blockchains that use mining models to secure their networks, and new mints often tend to update mining difficulty and reduce rewards over time. Mining difficulty increases when there are multiple miners operating on a blockchain.

Therefore, miners must buy specialized, expensive mining equipment to maintain competitiveness. The need to install a cooling system incurs additional costs. Finally, miners have to pay sky-high electricity bills to run and cool their equipment. With this in mind, mining operations are only profitable when the revenue generated is significantly higher than the amount spent on electricity and rig maintenance.
The rise of large mining companies makes it a lot more difficult to make a profit from a single mining company. These large mining companies have the capital to build mining farms (facilities designed to accommodate multiple mining rigs) in areas with cheap electricity and a mostly cold climate. That way, they increase their mining efficiency while reducing the cost of operating the farm.
With the above factors, Mining Solo quickly became redundant because the opportunity to find new blocks was very limited and costs continued to increase. Therefore, mining pools are considered a potential solution compared to Mining Solo.
What is a mining pool?
Due to the limitations of “mining alone” – Mining Solo, the mining sector has proposed a method of combining the hash power of individual miners to increase the probability of finding new blocks. This solution is called a Mining Pool or miners’ association. It is like a coordinated network of individual miners who gather together to synthesize their computing power to solve algorithms faster and more efficiently, enhancing the ability to successfully mine blockchain blocks to receive block rewards.
Rewards are shared among participants, resulting in lower incomes for each miner. However, due to the possibility that single miners are unable to mine even a single Block, it is still a priority for miners guild members to receive a smaller but more stable profit. Regular payments make mining pool operations more sustainable and attractive.
The function of the mining pool?
Usually, a miner’s association will place a coordinator responsible for organizing the members. They will ensure that miners are using different nonce numerical values so as not to waste hash power by trying to create the same blocks. These coordinators will also be responsible for dividing the rewards and returning them to the participants. There are many methods used to calculate and divide the work for each miner, as well as their respective rewards.
How does the mining pool work?
The simple example below will show how the Mining Pool model works:
Let’s say you and 99 other miners each own 0.01% of the total hash power of the whole network. That means:
- On average, you’ll be able to tap one block in every 10,000 blocks.
- With an average of 144 blocks mined each day, you can tap a block every 10 weeks.
This doesn’t mean you’ll be able to tap a block 10 weeks a week, it’s a probability. If you are unlucky, 20-50 weeks in a row you will have no income while still having to cover the costs of electricity and specialized mining equipment.
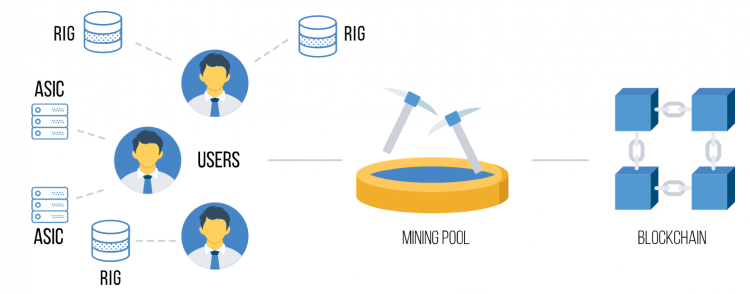
works In this case, you can join a digging group with 99 other people. If you all combine your hash power, your team will have a 1% Hash rate of the network. This means:
- For an average of 100 blocks, the team will find 1 Block, and possibly 2 blocks per day.
- Then the reward can be broken down and shared with all the miners involved.
How does the mining pool share profits?
Mining teams use a number of methods to share profits. The reward will depend on your share of the mining team’s output.
Note that the job share may be accepted or rejected by the team. Accepted sharing shows that the contribution of a team member has positively impacted the team’s chances of finding a new Block.
On the other hand, the rejected stake denotes work unrelated to the success of the Mining Pool. Even if the miner successfully completes the assigned tasks but is unable to meet the deposit deadline, their results do not affect the process of receiving the group’s coin, so their shares are rejected.
Understandably, the miners’ association rewards members based on their accepted stakes. You should fully understand the shared formula of a miner’s association before joining it or connecting your rig.
Here are two of the sharing methods commonly used by miners’ associations:
Pay-per-Share (PPS)
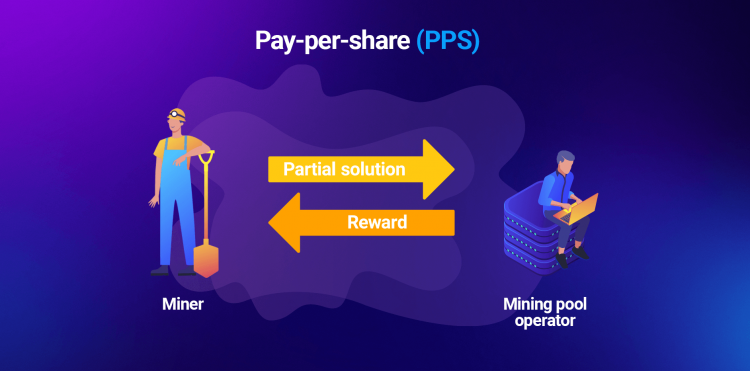
It is a form of providing instant fixed payments as members can withdraw income based on the number of accepted shares of them. Therefore, as long as the miners’ association recognizes your contribution, you don’t need to wait until a new Block is mined before withdrawing cash.
Pay-Per-Last-N-Shares (PPLNS)

It is a form of profit allocation based on the number of shares that the miner contributes. This type of attribution method is closely related to the blocks that are mined. If the Mining Pool exploits multiple blocks in a day, the miners will be highly profitable, if the mining pool is unable to mine a block throughout the day, the profitability of these miners for the whole month is zero. In the short term, the PPLNS model is highly correlated with the luck of the group. If your group is unlucky, the income of the team member will decrease, of course, the opposite can also happen. However, in the long run, the luck factor will not affect too much.
There are also two other common forms:
Pay Per Share+ (PPS+)
It is a mixture of two forms of PPS and PPLNS. Block rewards are settled according to the PPS model and transaction fees are paid under the PPLNS method. This means that in this mode, miners can get extra income from a portion of the transaction fee based on the PPLNS payment method.
Full Pay Per Share (FPPS)
In this form, both the regular block part and the mining service fee are paid according to the theoretical profit. Charge the standard transaction fee for a certain period of time and distribute it to miners according to their hash power contribution in the Mining Pool. It increases the miner’s income by sharing a portion of the transaction fee.
Are mining pools a threat to blockchain decentralization?
If a certain group gets 51% of the network’s hash power, they can launch a 51% attack. That will allow them to censor transactions and reverse old ones. Such an attack could cause major damage to the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
So, do miners’ associations increase the risk of attack by 51%? The answer is: maybe, but it’s also very unlikely.
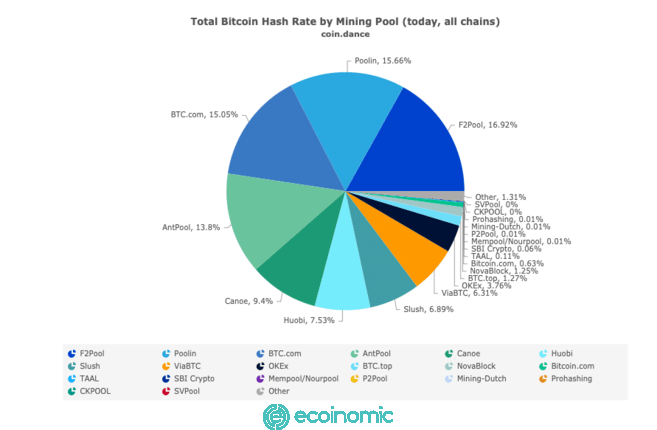
In theory, the top four forms of mining pools can collude to take control of the network. However, that won’t make much sense. Even if they try to carry out an attack, the price of Bitcoin will likely plummet because their actions will sabotage the system. As a result, any coins they buy will lose value.
Moreover, the group does not necessarily own mining equipment. Each individual directs their machine toward the coordinator’s server, but can also freely switch to other groups. It is in the best interests of both the participants and the operators of the miners’ association when the ecosystem is decentralized. After all, they can still make money if the mining is profitable.
There have been a few instances where miners’ associations have grown to the point where it can be considered a worrying size. Overall, the association (and miners in the society) have taken steps to reduce the hash rate.
Xem thêm: What Is Market Cap? Explain Crypto Market Capitalization In 2 Minutes
Advantages of Mining Pool
It can be said that the Mining Pool provides individuals with a new and effective method for participating in cryptocurrency mining. By combining computing power, miners can achieve a higher success rate without buying additional mining rigs or paying sky-high electricity bills.
On the other hand, the rewards created by mining groups are shared. Therefore, miners receive diminishing rewards. However, in the long run, Mining Pool tends to be a more stable and profitable venture than Mining Solo.
Disadvantages of Mining Pool
Participating in a miners’ association means that individuals have given up some of their autonomy during the mining process. They are often bound by the terms set by the Mining Pool itself. In addition, miners participating in the Mining Pool are also required to share any potential rewards.
Besides, a small number of mining pools such as AntPool, Foundry, USD Pool,… Dominating the Bitcoin mining process could be a threat to bitcoin’s decentralization.