Advertisement
What is ransomware?
Ransomware, also known as ransomware, is a form of malicious code (Malware) controlled by hackers. After infecting the computer, it prevents users from accessing and using their computer systems or document files. Most Ransomware hijacks and encrypts all the victim’s information it finds (Cryptolocker) or hides C&C packets on the computer (CTB Locker) These types of malware are often detected on the Windows operating system.
Ransomware has been considered by the U.S. Department of Justice to be a new model of cybercrime. It has the potential to have impacts on a global scale and cause huge impacts that can disrupt business operations and lead to data losses.
The ultimate goal is to extort decryption ransoms, which are often required in hard-to-track digital currencies such as Bitcoin or some other coins with a value of several to millions of dollars. However, victims have to accept that, even if they pay the hacker, they cannot get 100% of the data back.
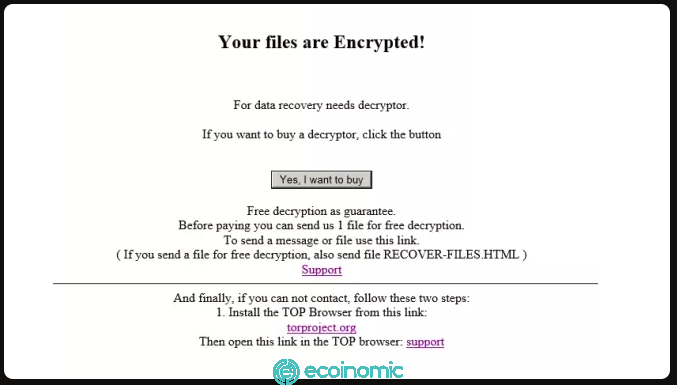
Organizations with poor security, highly affordable and fast organizations, or organizations with sensitive data are often targeted by ransomware.
Famous Ransomware Attacks
WannaCry
In 2017, WannaCry malware infiltrated and attacked more than 250,000 computers worldwide, estimating total damage to billions of dollars. Taking advantage of the Microsoft Windows vulnerability, the malware infiltrated the SMB protocol and automatically spread to other computers on the same network.
GandCrab
GandCrab is ransomware that is spread through online advertisements. When users click on the ad, they will be redirected to a landing page containing malicious code. To decrypt GandCrab, users must pay a ransom in Bitcoin or Dash via installing the Tor browser on a computer.
Some other ransomware attacks
A few quite famous attacks such as CryptoWall, Reveton, Fusob, CryptoLocker…
The history of the formation and development of ransomware
Ransomware was first detected between 2005 and 2006 in Russia. TrendMicro’s first reports were in 2006, with the TROJ_CRYZIP variant. A, a form of Trojan that, after infiltrating a user’s computer, instantly encrypts and compresses system files with a password, and creates *.txt files that require the victim to pay a $300 fee to retrieve personal data. It then attacks text files and systems such as * .DOC, *. XL, *.DLL, *.EXE…
In 2011, another form of ransomware, SMS Ransomware, was discovered with a different way of operating. It is the user who must send a message or make a phone call to the hacker’s phone number until the money transfer procedure is completed. This variant was discovered under the name TROJ_RANSOM. QOWA will continuously display fake notifications on the computer screen.
After that, the ransomware gradually spread out of Russia, first to the European region. By early 2012, TrendMicro had recorded numerous attacks across Europe (even in the US and Canada). Later, another variant spread very strongly in two main regions, France and Japan, along with the way the original ransomware worked.
By 2012, Reventon had developed new forms and tricks. It’s that they use local voice recordings to transmit extortion to victims instead of the old way of announcing them. The emergence of ransomware has a heavy impact on personal systems as well as enterprise networks.
The mechanism of a ransomware attack
Ransomware often spreads through spam or Phishing emails. They can also be through websites or drive-by downloads, and the ultimate goal is to break into the network. It is possible to summarize the mechanism of an attack through the following stages:
- Infection stage: Once sent to the system via a phishing email, it installs itself on the terminal and every network device it can access.
- Cryptographic Key Generation Stage: This software communicates with the command and control server operated by the cybercriminals behind the attack to generate cryptographic keys that are used on the local system.
- Encryption stage: It encrypts any data that can be found on local machines and networks.
- Exclusion stage: With encrypted data, it displays instructions on extortion and ransom payments, threatening to destroy the data if not paid.
- Unlocking stage: The victim pays the ransom in the hope that the data is not affected. However, this usually happens less. And in some cases, ransomware is installed along with the Trojan to have more control over the victim’s device.
Types of ransomware
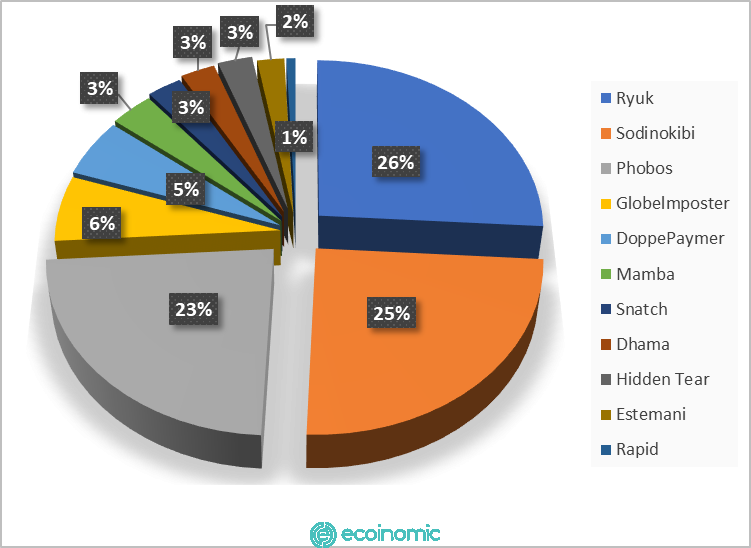
There are two main types of ransomware: Locker Ransomware (which locks computers and devices) and Crypto Ransomware (which prevents access to files or data, usually through encryption). The chart below is the latest ransomware types and their attack patterns latest types of ransomware and their attack patterns.
In addition, users also need to watch out for old ransomware such as CryptoLocker 2013, CryptoWall 2014, CTB-Locker 2014, TorrentLocker 2014, Bitcryptor and CoinVault 2015 and TeslaCrypt 2015…
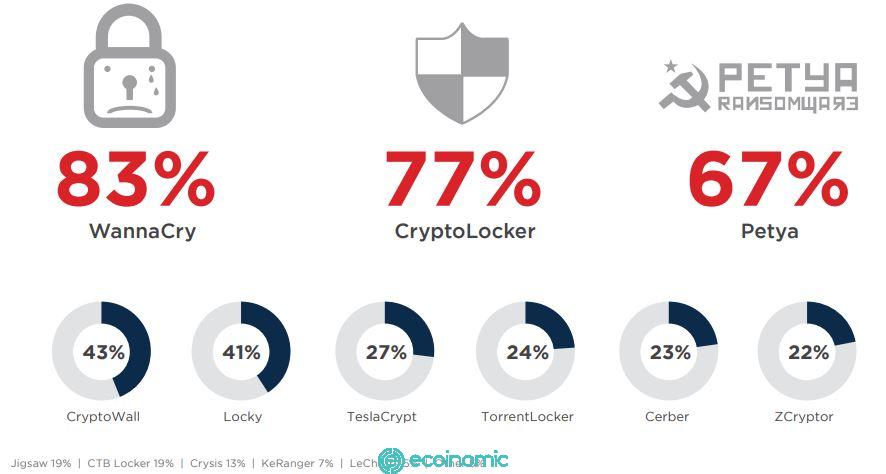
How to prevent ransomware
To protect data from the attack of ransomware, users can apply the following measures:
- Install antivirus software and make sure it’s up to date
- Apply software patches to keep systems up to date
- Change the default password regularly across all access points
- Equipped with the knowledge of email, skills to recognize suspicious emails
- Create many barriers and understand the connections on the network.
- There is always a backup using external sources
- Avoid access to unsecured websites

What to do if you are infected with ransomware?
Being attacked by ransomware is something no user wants, but if you know how to handle it, you can minimize the damage.
Isolate, separate networks and systems
The first step to control the Ransomware outbreak is to isolate infected systems from the rest of the network. Turn off the systems and pull out the network cable and turn off wifi. Infected systems should be completely isolated from computers and other storage devices on the network.
Identify and Delete Ransomware
Next, find out what kind of malware infected the computers. Incident response teams, organizations, or external consultants are the addresses users can visit. They can identify the strain and start planning the best way to deal with the spread.
Delete an infected machine and restore from a backup
To ensure that no malicious code is hidden in the system, it is recommended to delete all data and then restore everything from a secure backup. Learning from shortcomings is one of the good ways to understand the nature of the attack and prevent similar attacks from happening again.
Conclusion
For Nodes delivered in the Blockchain network, data security is extremely important. Because this is where the system is stored and regulated along with other intersections. Being attacked by Ransomware can have unpredictable consequences, can even cause heavy financial damage and cause the system to collapse.
See also: What is leverage in cryptocurrency trading and how to use it?