Advertisement
What is Sidechain?
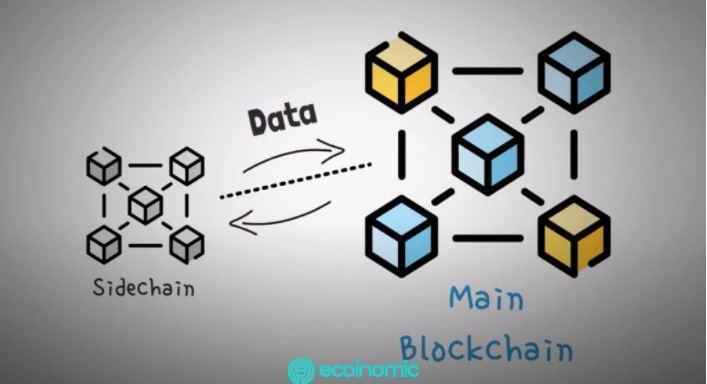
Sidechain is a separate blockchain but not a standalone platform. Because somehow it’s still linked to the main chain. The main chain and Sidechain can interact with each other and the asset can run freely from one chain to another. Sidechain’s function is to increase the potential and enrich the existing Blockchain.
The Sidechain has its own consensus mechanisms, usually, Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), or Proof of Author (PoA). Scaling solutions such as Sidechain (in addition to Plasma and rollups) are classified as Layer 2 solutions because they are built on Layer 1.
Sidechains allow investors to send their tokens from the main chain and receive them. Money that has been transferred to Sidechain can be used in this ecosystem. Besides, investors can also withdraw their tokens back to the main chain. Such token transfer is called a 2-way peg or 2-way bridge.
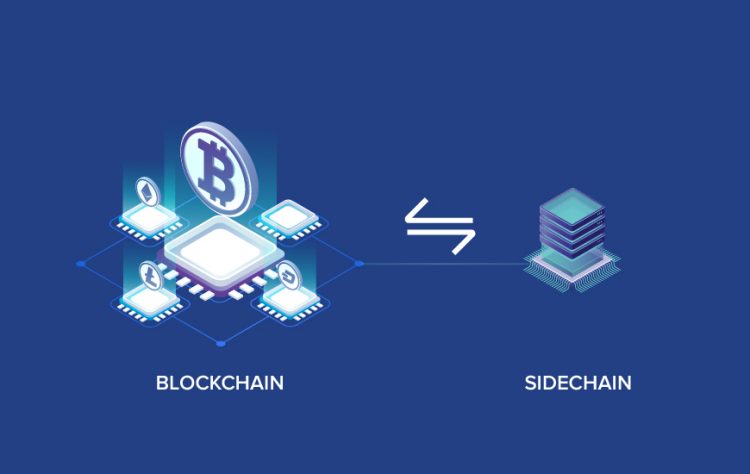
Money is always guaranteed to be transferred in a number of ways. Sometimes, the property is transferred from the main chain to a special address. They were not actually sent to but were locked to the address and a corresponding amount was released on Sidechain. More simply, the asset is sent to the supervisor and this person will exchange the deposit for money on the sidechain. In addition, the exchange rate of assets between blockchain and sidechain will usually be predetermined.
How does the sidechain work?
To use Sidechain, investors must send their funds from the main chain to an output address. Money to the output address will be locked. This means that investors will not be able to use their money anywhere else.
The contact information will be sent through the main chain when the investor’s money is transferred to the output address and after a period of authenticating the information. This is a measure to ensure, enhance security. After the end of the waiting period, a corresponding amount of money will be disbursed on Sidechain. At this point, investors can use their money.
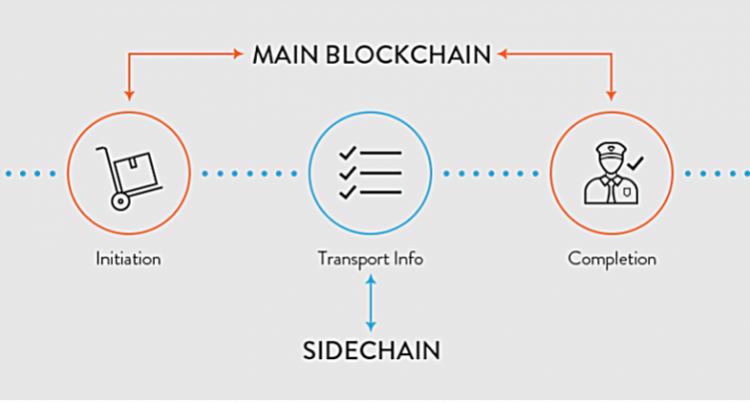
When you want to do the opposite, the investor also transfers his funds from Sidechain to the output address (where the money is locked).
After the end of the information authentication period, the corresponding amount will be transferred to the main blockchain to make the transaction.
See also: What Is Binance? Binance Registration Guide
Advantages and disadvantages of Sidechain
Advantages
- Long-term: Investors only need to create Sidechain once, it is maintained and used by anyone.
- Highly interactive: Sidechain allows investors to interact between different cryptocurrencies. Publishers always check for software upgrades as well as beta releases before they are released on the main chain.
- Utility: Sidechain has features that are superior to other forms, which can offer fast transactions at a lower cost.
- Upgrade capability: Sidechain can upgrade and deploy testing without broad consensus. Meanwhile in blockchain, upgrading a blockchain will be difficult with the requirement to have a high consensus.
- Diversification: The sidechain provides investors with a place to exchange assets off the main chain. This helps investors diversify their experience.
Disadvantages
- Security: Funds locked in the main chain or Sidechain all depend on the security of the entire process. Although there is already verification of information, hackers can attack any component of the process. Link posts can be seen as an ideal place for hackers to attack the process.
- Authenticity: It’s a sidechain spoof. A third party can create a chain separate from the main blockchain and then defraud investors in the smart contract.
- Cost: Although compared to other transactions, Sidechain already has a cheaper cost, it needs secure miners so it needs a big cost for security. In addition, forming a Sidechain also requires a huge amount of money.
See also: What Is Proof Of Stake? How Does PoS Work?
Sidechain’s technology
- Link point
A linked point is a group of servers that act as a point between the main chains and sidechain. The link point is the component that determines when the investor’s money is locked as well as disbursed. Sidechain developers can select members of the link point. The biggest disadvantage of the link point can be mentioned in that they form another layer between the sidechain and the main chain.
- Security
The biggest advantage of Sidechain is that they are secure with the main chain. Sidechain secures its own security and handles issues that arise without affecting the main chain. Similarly, a security issue on the main chain does not affect the sidechain’s security. However, this can cause the value of the peg to be greatly reduced.
In addition, Sidechain requires having its own miner. Miners can receive many incentives thanks to consolidated training. Merging mining is a place where two different cryptocurrencies but the same algorithm can mine at the same time.
Why are sidechains used?
There are many reasons why employers choose Sidechain as a primary method of money transfer.
- First, Sidechain has features that Bitcoin can’t get. Blockchain is a carefully designed exchange system. Although Bitcoin is the most decentralized and cryptocurrency, in terms of throughput, it’s not the best. There’s no denying that Bitcoin transactions are faster than conventional methods, but compared to blockchain systems, Bitcoin is still quite slow. In addition, the cost can increase significantly when the network is blocked.
- Second, Sidechain is not bound by the same rules. In fact, it doesn’t even need to use Proof of Work to work. Investors can use any consensus mechanism, having full confidence in a security validation process. What’s more, investors can add upgrades that don’t exist in the main chain, create larger blocks, and make quicker settlements.
- Third, Sidechain may experience serious errors but do not affect the main chain. This allows investors to use the platform to experiment and come up with features that may be highly consensual.
- Fourth, if an investor is willing to trade, Sidechain could be an important step toward increasing scalability effectively. the Nodes at the main chain do not need to store every transaction from Sidechain. For example, when a Bitcoin investor wants to transfer an amount of Bitcoin for 5 equivalent coins on a Sidechain, he only needs a single Bitcoin transaction in the main blockchain, making hundreds of transactions at sidechain then logging out. On the main blockchain, he only performs 2 operations: log in and log out.
Conclusion
Sidechain is a private blockchain linked to the main blockchain. They do an ancillary network that performs the additional functions of the main blockchain: faster transactions, lower transaction costs, greater scalability in terms of the number of transactions.
Sidechain is expected by crypto investors to bring a significant improvement in scalability to the current blockchain. In the future, there are many users participating in the network, it is important at that time to maintain decentralization.
At that time, the problem of improving security, optimizing procedures and enforcing limits on the growth of blockchain so that new nodes can be easily joined needs to be quickly solved. Sidechain developers believe that, when the problem is solved, the chain will only be used to solve high-value transactions, close logins, log out of Sidechain or open the channel.